Endocannabinoid System (ECS)
I wanted to talk about Cannabinoids and the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) and why I think it's important to you.
My CBD & ECS Story
Three years ago I had a heart attack and was ordered by doctors to make some drastic lifestyle changes, including giving up smoking.
I was obviously anxious about my health, but also eager to find something to fill the void left by my 20-a-day habit when, on a business trip to the States, I found pure cannabidiol (CBD) distillate vape juice. In short, this discovery changed my life and I made it my mission to produce the same high-quality CBD here in the UK.
Whereas many other sellers here in the UK buy their CBD from a wholesaler, add thinning agents such as VG or PG (for vapes and juices), before sticking their own label on it for re-selling, from the start I’ve been committed to producing my own premium pure broad spectrum triple distilled CBD.
Woodies & CBD
I use 100% pure CBD distillate throughout my range, produced by myself using clean solvent extraction and purification techniques, resulting in a completely pure and natural plant-derived extract. This is then combined with 100% natural cannabis-derived terpenes for the all-important entourage effect that broad-spectrum, as opposed to isolate, CBD offers - put simply, this means that the different plant components work better together than separately.
CBD & ECS
With a growing body of research indicating that CBD interacts with the body’s own endocannabinoid system (ECS) and has the potential to treat many conditions including epilepsy and MS, I decided I needed to know exactly how CBD influences the ECS. So I completed a college qualification and this is what I found out...
CBD is a family of more than 100 compounds
Accounting for up to 40% of its make up, the cannabinoid CBD is one of over 100 compounds in the cannabis plant. Unlike THC, the other main cannabinoid present in the plant, CBD is not psychoactive and won’t get you high. This is why it was legalised in 2016, whereas THC remains illegal. The reason why the two cannabinoids affect us differently is down to the ways in which they interact with our ECS.

ESC the Bodies Cell-signalling System
Although initially identified in the early 90s by researchers looking into the effects of THC, the endocannabinoid system is a complex cell-signalling system that does NOT depend on cannabis use for its functions within the body. The ECS actually contains many cannabinoids of its own called endocannabinoids, whereas both CBD and THC are phytocannabinoids that occur naturally in the cannabis plant. Although it’s still not fully understood, research has shown that the principal function of the ECS is to achieve homeostasis - or balance - within the body as a whole by influencing and regulating many physiological functions and processes relating to pain, inflammation, immune response, digestion and mood, to name but a few.

An example of this is if you are in pain or have a fever, for example, this could be a sign that you have some kind of imbalance within your body, so the ECS sends messages to different parts of the body telling them to take action to reduce the pain and fight the fever or inflammation, which helps to restore balance in your body and make you feel better.
The 3 Elements of ECS
The three main elements of the ECS are endocannabinoids, endocannabinoid receptors and enzymes, all of which carry out different roles in these processes.
Read More: Cannabigerol (CBG)
1. Endocannabinoids
The two main endocannabinoids within this system are anandamide (AEA) and 2-arachidonoylglyerol (2-AG) whose roles are to ensure internal functions run smoothly. Because they’re produced by the body as needed, it’s hard to know how much of each is typically present within our systems. However, there is a theory that people who have low levels endocannabinoids in their body - something referred to as endocannabinoid deficiency - could be more likely to develop certain difficult to treat conditions such as migraines, fibromyalgia and irritable bowel syndrome.
2. Endocannabinoid Receptors
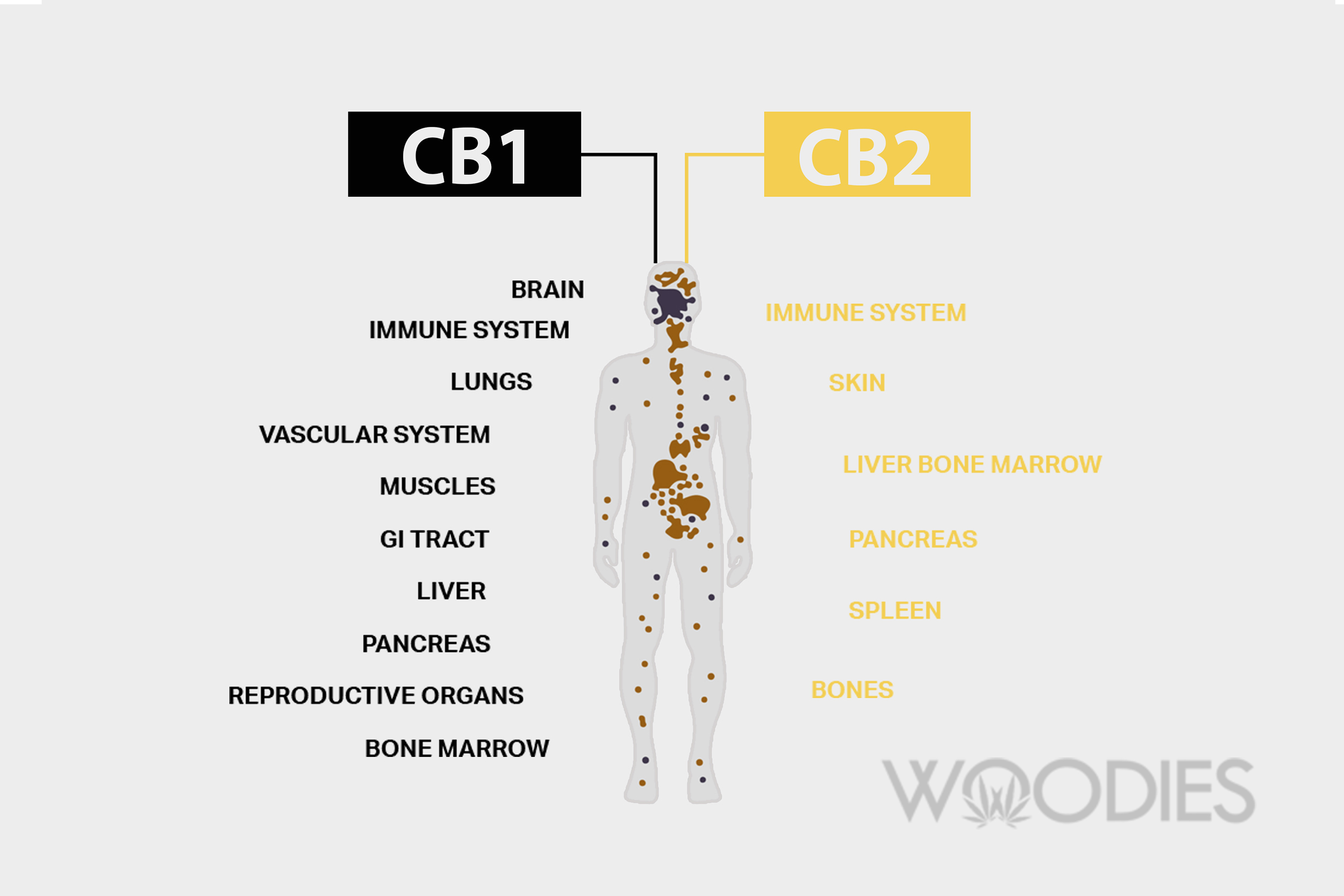
Endocannabinoids bind to the endocannabinoid receptors throughout our body and, when needed, prompt the ECS into action. The two main endocannabinoid receptors are CB-1 (located mainly within the central nervous system) and CB-2 (located mainly in the peripheral nervous system).
When we are ill or in pain, the amount of CB1 receptors in our body increases which aids in the management and reduction of inflammation, pain and nausea. So, according to research carried out on both animals and cancer sufferers, they help to make us feel not quite as bad as we otherwise would.
Because CB2 receptors are present in the immune system, they can modulate and suppress its function when needed, for example, to reduce excessive pain and inflammation, to reduce allergic reaction or to stimulate immune cells to clear out bacteria.
Different cannabinoids are able to bind to both types of receptors with different results. For example, some might bind to a CB-1 receptor in a spinal nerve to relieve pain, while others might bind with CB-2 receptors in immune cells to signal that there is inflammation - and then the endocannabinoid system will deal with it in the appropriate way.
3. Enzymes
The role of enzymes is to break down endocannabinoids once they’ve performed their purpose. The two main ones being fatty acid amide hydrolase (breaks down AEA) and monoacylglycerol acid lipase (breaks down 2-AG).
These interactions with the ECS influence the way in which the brain releases neurotransmitters to send messages to and between cells in the body, meaning they play a part in many ECS processes, including pain management, immune function, stress reduction and the promotion of sleep.
Just like the endocannabinoids in our body, the cannabinoids CBD and THC also interact with the endocannabinoid receptors in our body.
CBD & THC; The Differences
However, despite having an identical molecular structure, CBD and THC are each arranged in a different way which is why they make the body react in different ways.
THC
Whereas THC binds with the brain’s CB1 receptors to produce a “high”, CBD doesn’t appear to function in this way and can even help to prevent THC bonding to them, lessening its psychotropic effects.
THC binds to both CB1 and CB2 receptors and its effects on both the mind and body can be powerful and at times unwanted. For example, although it may reduce pain it can also cause paranoia and anxiety in some people and scientists are currently attempting to formulate synthetic THC cannabinoids that only interact with the ECS in desirable ways to eliminate the unwanted side effects.
CBD
According to experts, CBD doesn’t bind to the CB1 and CB2 receptors. Instead, it’s believed that CBD actually interacts with the cannabinoids already present within the ECS, helping to influence their functions and slowing their breakdown, which is thought to explain its ability to help treat a number of conditions and illnesses. Some scientists think that it actually binds to a yet to be discovered receptor, although more research is needed if we are to discover exactly how this cannabinoid works in so many amazing ways.
Luckily, the body of anecdotal and clinical evidence about the benefits of CBD is ever increasing, so watch this space to find out more!
---
References:
- A Simple Guide to the Endocannabinoid System, C. Raypole, 7/05/19. https://www.healthline.com/Health/endocannabinoidsystem
- The Endocannabinoid System and it’s Therapeutic Exploitation, V. Do Marzo, M. Bifulco, L. De Petrocellis, September 2004.
- Clinical Endocannabinoid Deficiency Reconsidered: Current Research Supports the Theory in Migraine, Fybromyalgia, Irritable Bowel, and Other Treatment-Resistant Syndromes, E. B. Russo, Cannabis Cannabinoid Red: 2016; (1): 154-165, 1/07/19. ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Human Endocannabinoid System (n.d.)
Disclaimer
→ This article is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any ailment, illness or disease.
→ For a full report on the recreational use of CBD read WHO's Critical Review Report on CANNABIDIOL (CBD)
If you’ve found this helpful, please share. And if you have any further questions, please let me know below and I or one of my team will do our best to provide you with answers.
Jx
Jamie Wood, Founder & CEO
Related Post
I’ve made it my business to know about Cannabidiol or CBD as it’s most commonly known. Woodies help treat stress and pain with our CBD Oils.

